The sintering system of the cement plant has been operating at high temperatures for a long time. Choosing a better insulation material can effectively reduce heat dissipation by lowering the shell temperature without increasing or even reducing the insulation thickness. In order to maintain a better thermal condition of the system, thereby reducing energy consumption, reducing production costs, achieving the goals of energy conservation, environmental protection, and increasing production and efficiency.
The traditional custom for thermal insulation materials in fired systems is to choose microporous calcium silicate boards or ceramic fiber boards. Its thermal insulation performance can no longer meet the current higher needs for thermal insulation and energy saving. New nano-scale microporous thermal insulation materials, referred to as nano-thermal insulation materials, provide technical and material support for the higher requirements for thermal insulation and energy saving of cement kiln firing systems and the improvement of system production capacity.

Micro-nano Thermal Insulation Materials for Cement Kilns
Recently, cement companies have replaced the original insulation materials of cement burning systems with nano-insulation materials. A good thermal insulation effect has been achieved, which can be used as a reference for other cement companies.
Thermal insulation of the cyclone of the cement kiln preheating and predecomposition system
The cyclone of the preheating and predecomposition system of a cement company was originally insulated with 114mm refractory bricks and 112mm calcium silicate boards. In order to enhance the heat insulation effect of the refractory lining, the company repaired the cyclone on the east side of Line 3 C5. 25 mm nano-insulation boards were used to replace the original calcium silicate boards of the same thickness, keeping the total thickness of the thermal insulation lining unchanged at 112 mm, and the remaining calcium silicate boards with a thickness of 87 mm were used.

C5 cyclone insulation lining transformation effect. It was discovered after a period of time that the original calcium silicate board was replaced with nano-insulation board. The heat dissipation loss of the C5 cyclone is reduced by 336W/m2, the shell temperature drops by 21°C, and the heat loss is reduced by 43%. The thermal insulation effect of the refractory lining has been improved.
Improvement of the heat insulation layer in the pre-decomposition zone behind the transition zone of cement rotary kiln
Another cement company’s new special cement line project is to reduce the shell temperature of the rotary kiln’s pre-decomposition zone. In the pre-decomposition zone after the transition zone of the rotary kiln, new nano-insulation panels and grooved brick structures are used to replace the traditional insulation structure. During on-site construction, a 15 mm thick nano-insulation board is inserted into the grooved bricks to form a thermal insulation layer between the rotary kiln shell and the refractory bricks.

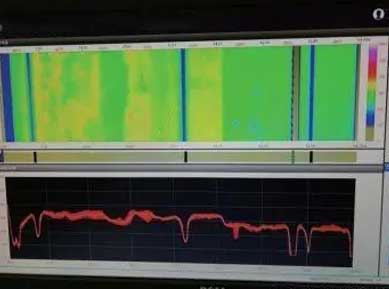
The production line uses 15 mm thick nano-insulation panels. Ten days after ignition and production, during normal production of the rotary kiln, the temperature scan of the rotary kiln shell at 35 to 63 m was all green low-temperature areas, and there was no transition color between the two connected areas. It fully reflects the heat insulation effect of the grooved brick composite nano-insulation board. Compared with traditional insulation methods, the surface temperature of the cylinder is reduced by 110°C. The heat dissipation loss is reduced by 4785W/m2, and the annual heat dissipation loss is reduced by 870,000 yuan. The investment can be recovered in about 2 months. Thermal insulation effect of rotary kiln preheat zone.
Regular maintenance and replacement of refractory bricks and thermal insulation lining in the transition zone of the cement rotary kiln
When a cement company was regularly repairing and replacing refractory bricks in two rotary kiln transition zones, it decided to use grooved bricks combined with 15 mm thick nano-insulation panels to reduce the temperature of the shell of the rotary kiln transition zone. After a period of construction, according to theoretical calculations, the shell temperature of the transition zone of the traditional refractory brick rotary kiln can be reduced by 70 to 110°C. It can greatly reduce the ovality deformation of the rotary kiln shell and reduce energy consumption.
Rongsheng Micro-nano Thermal Insulation Board
Rongsheng Kiln Refractory Factory has accumulated rich experience in the application of thermal insulation materials in various industries. In order to reduce the outer wall temperature of high-energy-consuming and high-temperature industrial furnaces and save production costs, micro-nano thermal insulation materials have been introduced. It better meets the needs of the domestic market and solves many domestic and worldwide thermal insulation problems.

Nano-thermal insulation material is a nano-scale microporous thermal insulation material produced by using nanotechnology, adding unique anti-infrared radiation materials, and adopting a special process. Compared with traditional micron-sized pore insulation materials such as ceramic fibers and microporous calcium silicate boards, the pores of nano-insulation materials are around 20 nm. The thermal insulation performance at the same temperature is 4 times better than traditional insulation materials.
So far, it has been unanimously proven by many cement companies that the use of nano-insulation materials in the rotary kiln firing system can significantly reduce the heat loss of the rotary kiln barrel. Reducing the kiln operating load and achieving energy saving and consumption reduction are worthy of further research and promotion.